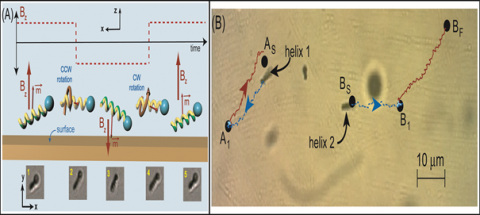
We have developed a novel technique to achieve independent motion of magnetic micro/nanoswimmers. The method uses oscillating magnetic field to actuate micron sized helical structures that show reciprocal motion with enhanced diffusivity [1]. The motile nanostructures can be used as a model system to study active matter. By superposing orthogonal dc magnetic field with the oscillating fields, we could manuever and position the helical structures individually[2]. We have developed a novel technique to achieve autonomous motion of magnetic micro/nanoswimmers. The method uses oscillating magnetic field to actuate micron sized helical structures that show reciprocal motion with enhanced diffusivity [1]. The motile nanostructures can be used as a model system to study active matter. By superposing orthogonal dc magnetic field with the oscillating fields, we could manuever and position the helical structures individually[2].
Fig (A) Schematics of reciprocal swimming. (B) Experimental demonstration of independent positioning, where oscillating, dc and rotating magnetic fields are used to move the helices in different directions, and positioned them independently. After the different actuation steps, the position of helix-1 remains unchanged while helix-2 moves to a position as determined by the direction of magnetization, magnetic field and frequency.
[1] Pranay Mandal, and Ambarish Ghosh. "Observation of enhanced diffusivity in magnetically
powered reciprocal swimmers." Physical review letters 111.24 (2013): 248101.
[2] Pranay Mandal, Vaishali Chopra, and Ambarish Ghosh. "Independent positioning of magnetic
nanomotors." ACS nano 9.5 (2015): 4717-4725.
